publications
publications by categories in reversed chronological order, please check my google scholar page for full details.
2024
-
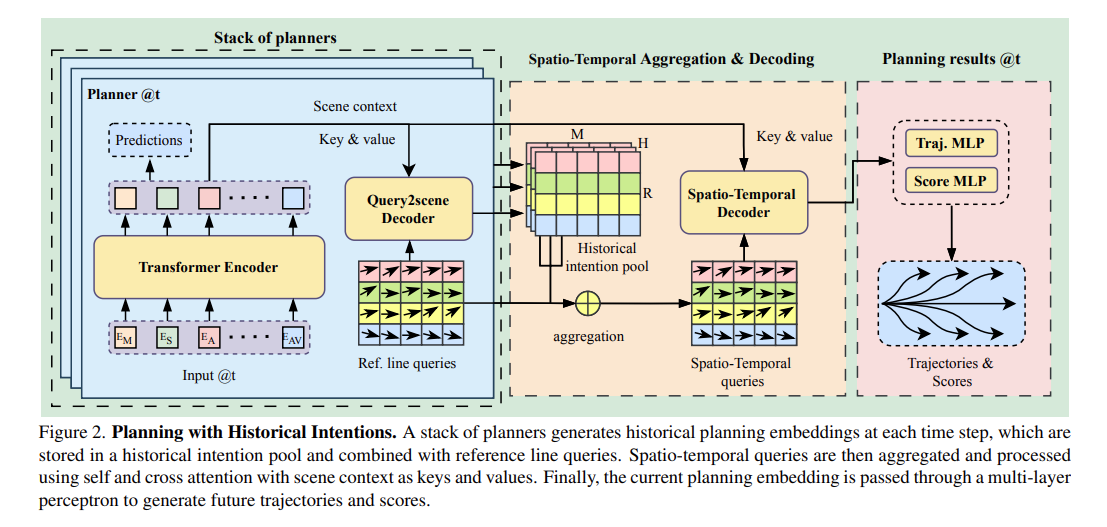 LHPF: Look back the History and Plan for the Future in Autonomous DrivingSheng Wang, Yao Tian, Xiaodong Mei, Ge Sun, Jie Cheng, and 3 more authors2024[Under review]
LHPF: Look back the History and Plan for the Future in Autonomous DrivingSheng Wang, Yao Tian, Xiaodong Mei, Ge Sun, Jie Cheng, and 3 more authors2024[Under review]Decision-making and planning in autonomous driving critically reflect the safety of the system, making effective planning imperative. Current imitation learning-based planning algorithms often merge historical trajectories with present observations to predict future candidate paths. However, these algorithms typically assess the current and historical plans independently, leading to discontinuities in driving intentions and an accumulation of errors with each step in a discontinuous plan. To tackle this challenge, this paper introduces LHPF, an imitation learning planner that integrates historical planning information. Our approach employs a historical intention aggregation module that pools historical planning intentions, which are then combined with a spatial query vector to decode the final planning trajectory. Furthermore, we incorporate a comfort auxiliary task to enhance the human-like quality of the driving behavior. Extensive experiments using both real-world and synthetic data demonstrate that LHPF not only surpasses existing advanced learning-based planners in planning performance but also marks the first instance of a purely learning-based planner outperforming the expert. Additionally, the application of the historical intention aggregation module across various backbones highlights the considerable potential of the proposed method. The code will be made publicly available.
@misc{LHPF, title = {LHPF: Look back the History and Plan for the Future in Autonomous Driving}, author = {Wang, Sheng and Tian, Yao and Mei, Xiaodong and Sun, Ge and Cheng, Jie and Ma, Fulong and Sander, Pedro V. and Liang, Junwei}, year = {2024}, eprint = {2411.17253}, archiveprefix = {arXiv}, primaryclass = {cs.RO}, note = {[Under review]}, url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.17253} } -
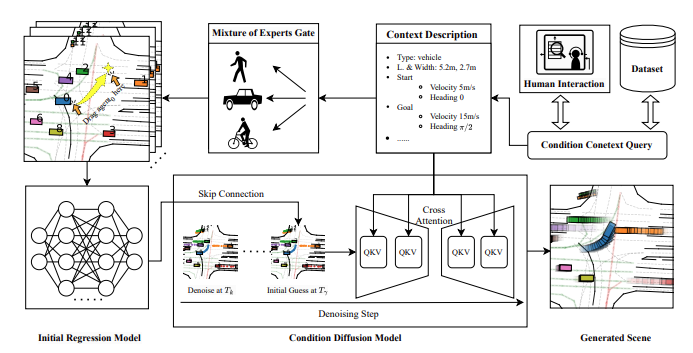 DragTraffic: Interactive and Controllable Traffic Scene Generation for Autonomous DrivingSheng Wang, Ge Sun, Fulong Ma, Tianshuai Hu, Qiang Qin, and 3 more authorsIn 2024 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2024
DragTraffic: Interactive and Controllable Traffic Scene Generation for Autonomous DrivingSheng Wang, Ge Sun, Fulong Ma, Tianshuai Hu, Qiang Qin, and 3 more authorsIn 2024 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2024Evaluating and training autonomous driving systems require diverse and scalable corner cases. However, most existing scene generation methods lack controllability, accuracy, and versatility, resulting in unsatisfactory generation results. Inspired by DragGAN in image generation, we propose DragTraffic, a generalized, interactive, and controllable traffic scene generation framework based on conditional diffusion. DragTraffic enables non-experts to generate a variety of realistic driving scenarios for different types of traffic agents through an adaptive mixture expert architecture. We employ a regression model to provide a general initial solution and a refinement process based on the conditional diffusion model to ensure diversity. User-customized context is introduced through cross-attention to ensure high controllability. Experiments on a real-world driving dataset show that DragTraffic outperforms existing methods in terms of authenticity, diversity, and freedom.
@inproceedings{10801623, author = {Wang, Sheng and Sun, Ge and Ma, Fulong and Hu, Tianshuai and Qin, Qiang and Song, Yongkang and Zhu, Lei and Liang, Junwei}, booktitle = {2024 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS)}, title = {DragTraffic: Interactive and Controllable Traffic Scene Generation for Autonomous Driving}, year = {2024}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {14241-14247}, keywords = {}, url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.12624}, doi = {10.1109/IROS58592.2024.10801623} } -
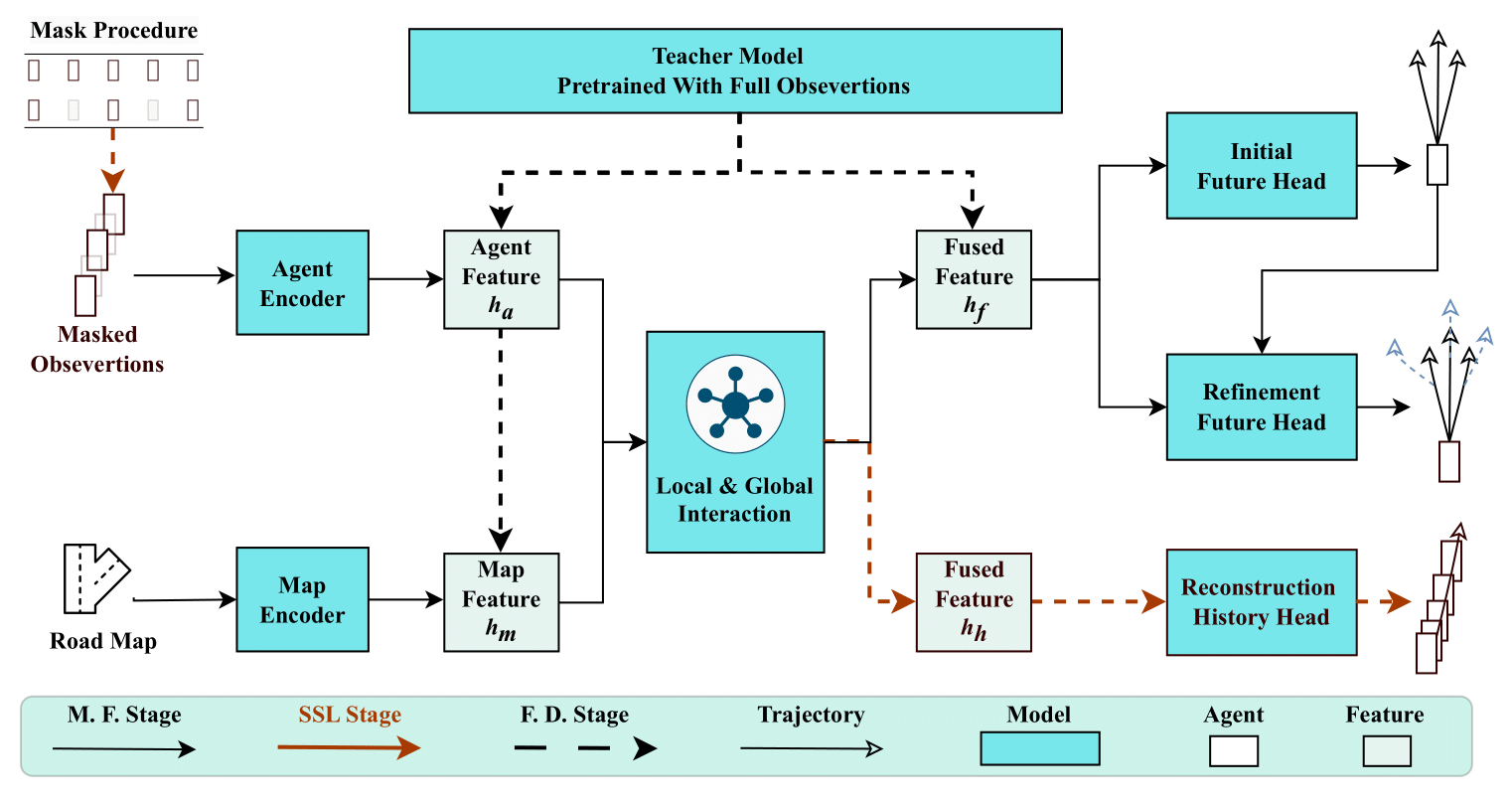 Improving Autonomous Driving Safety with POP: A Framework for Accurate Partially Observed Trajectory PredictionsSheng Wang, Yingbing Chen, Jie Cheng, Xiaodong Mei, Ren Xin, and 1 more authorIn 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2024
Improving Autonomous Driving Safety with POP: A Framework for Accurate Partially Observed Trajectory PredictionsSheng Wang, Yingbing Chen, Jie Cheng, Xiaodong Mei, Ren Xin, and 1 more authorIn 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2024Accurate trajectory prediction is crucial for safe and efficient autonomous driving, but handling partial observations presents significant challenges. To address this, we propose a novel trajectory prediction framework called Partial Observations Prediction (POP) for congested urban road scenarios. The framework consists of two key stages: self-supervised learning (SSL) and feature distillation. POP first employs SLL to help the model learn to reconstruct history representations, and then utilizes feature distillation as the fine-tuning task to transfer knowledge from the teacher model, which has been pre-trained with complete observations, to the student model, which has only few observations. POP achieves comparable results to topperforming methods in open-loop experiments and outperforms the baseline method in closed-loop simulations, including safety metrics. Qualitative results illustrate the superiority of POP in providing reasonable and safe trajectory predictions.
@inproceedings{POP, author = {Wang, Sheng and Chen, Yingbing and Cheng, Jie and Mei, Xiaodong and Xin, Ren and others}, booktitle = {2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA)}, title = {Improving Autonomous Driving Safety with POP: A Framework for Accurate Partially Observed Trajectory Predictions}, year = {2024}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {14450-14456}, keywords = {Accuracy;Roads;Self-supervised learning;Predictive models;Trajectory;History;Task analysis}, doi = {10.1109/ICRA57147.2024.10610154} } -
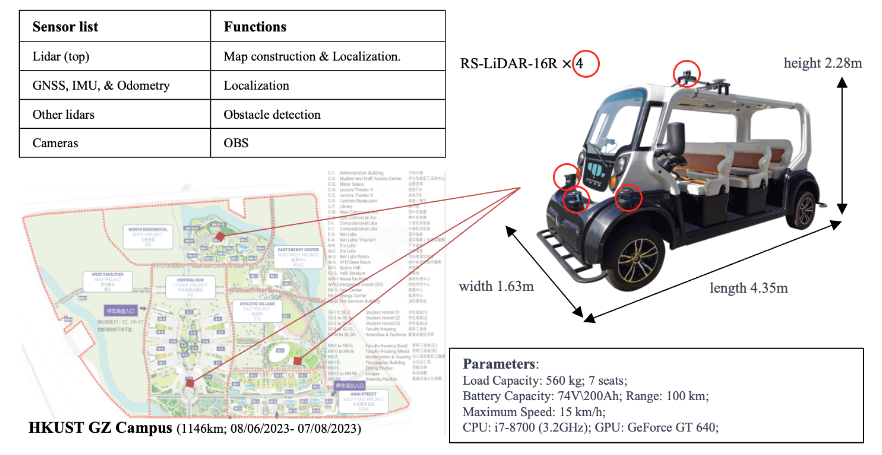 Enhancing Campus Mobility: Achievements and Challenges of the Snow Lion Autonomous ShuttleYingbing Chen, Jie Cheng, Sheng Wang, and othersIEEE Robotics & Automation Magazine, 2024
Enhancing Campus Mobility: Achievements and Challenges of the Snow Lion Autonomous ShuttleYingbing Chen, Jie Cheng, Sheng Wang, and othersIEEE Robotics & Automation Magazine, 2024In recent years, the rapid evolution of autonomous vehicles (AVs) has reshaped global transportation systems, leading to an increase in autonomous shuttle applications in people’s daily lives. Leveraging the accomplishments of our earlier endeavor, particularly Hercules [1], an autonomous logistics vehicle for transporting goods, we introduce Snow Lion, an autonomous shuttle vehicle specifically designed to transform on-campus transportation, providing a safe and efficient mobility solution for students, faculty, and visitors.
@article{RAM, author = {Chen, Yingbing and Cheng, Jie and Wang, Sheng and others}, journal = {IEEE Robotics & Automation Magazine}, title = {Enhancing Campus Mobility: Achievements and Challenges of the Snow Lion Autonomous Shuttle}, year = {2024}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {2-13}, keywords = {Laser radar;Task analysis;Sensors;Point cloud compression;Location awareness;Three-dimensional displays;Planning}, doi = {10.1109/MRA.2024.3433168} } - A Generic Trajectory Planning Method for Constrained All-Wheel-Steering RobotsRen Xin, Hongji Liu, Yingbing Chen, Sheng Wang, and othersIn IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2024[IROS2024 Accepted]
@inproceedings{xin2024generictrajectoryplanningmethod, author = {Xin, Ren and Liu, Hongji and Chen, Yingbing and Wang, Sheng and others}, booktitle = {IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems}, title = {A Generic Trajectory Planning Method for Constrained All-Wheel-Steering Robots}, year = {2024}, note = {[IROS2024 Accepted]}, } - DHP-Mapping: A Dense Panoptic Mapping System with Hierarchical World Representation and Label Optimization TechniquesTianshuai Hu, Jianhao Jiao, Yucheng Xu, Hongji Liu, Sheng Wang, and 1 more authorIn IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2024[IROS2024 Accepted]
@inproceedings{hu2024dhp, author = {Hu, Tianshuai and Jiao, Jianhao and Xu, Yucheng and Liu, Hongji and Wang, Sheng and others}, booktitle = {IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems}, title = {DHP-Mapping: A Dense Panoptic Mapping System with Hierarchical World Representation and Label Optimization Techniques}, year = {2024}, note = {[IROS2024 Accepted]}, } - IR-STP: Enhancing Autonomous Driving With Interaction Reasoning in Spatio-Temporal PlanningYingbing Chen, Jie Cheng, Lu Gan, Sheng Wang, Hongji Liu, and 2 more authorsIn IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2024
@inproceedings{IR-STP, title = {IR-STP: Enhancing Autonomous Driving With Interaction Reasoning in Spatio-Temporal Planning}, author = {Chen, Yingbing and Cheng, Jie and Gan, Lu and Wang, Sheng and Liu, Hongji and Mei, Xiaodong and others}, booktitle = {IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems}, year = {2024}, }
2023
-
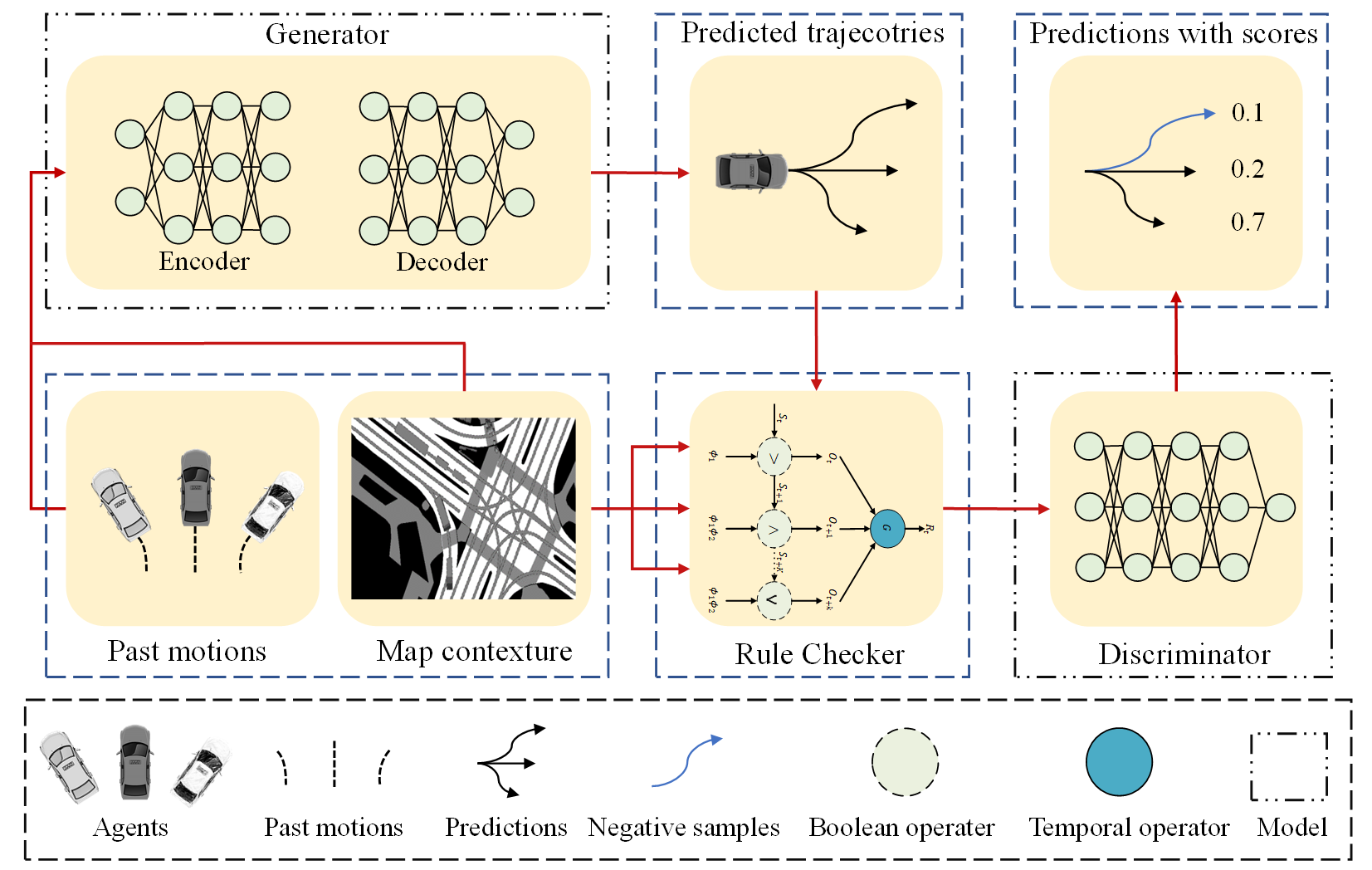 FCUS: Traffic Rule-Aware Vehicle Trajectory Forecasting Using Continuous Unlikelihood and Signal Temporal Logic FeatureSheng Wang, Ren Xin, Jie Cheng, and othersIn 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), 2023
FCUS: Traffic Rule-Aware Vehicle Trajectory Forecasting Using Continuous Unlikelihood and Signal Temporal Logic FeatureSheng Wang, Ren Xin, Jie Cheng, and othersIn 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), 2023@inproceedings{FCUS, author = {Wang, Sheng and Xin, Ren and Cheng, Jie and others}, booktitle = {2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO)}, title = {FCUS: Traffic Rule-Aware Vehicle Trajectory Forecasting Using Continuous Unlikelihood and Signal Temporal Logic Feature}, year = {2023}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {1-6}, keywords = {Biological system modeling;Neural networks;Predictive models;Trajectory;Safety;Forecasting;Task analysis}, doi = {10.1109/ROBIO58561.2023.10354968} } - Self-Supervised Drivable Area Segmentation Using LiDAR’s Depth Information for Autonomous DrivingFulong Ma, Yang Liu, Sheng Wang, and othersIn 2023 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2023
Drivable area segmentation is an essential component of the visual perception system for autonomous driving vehicles. Recent efforts in deep neural networks have sig-nificantly improved semantic segmentation performance for autonomous driving. However, most DNN-based methods need a large amount of data to train the models, and collecting large-scale datasets with manually labeled ground truth is costly, tedious, time consuming and requires the availability of experts, making DNN-based methods often difficult to implement in real world applications. Hence, in this paper, we introduce a novel module named automatic data labeler (ADL), which leverages a deterministic LiDAR-based method for ground plane segmentation and road boundary detection to create large datasets suitable for training DNNs. Furthermore, since the data generated by our ADL module is not as accurate as the manually annotated data, we introduce uncertainty estimation to compensate for the gap between the human labeler and our ADL. Finally, we train the semantic segmentation neural networks using our automatically generated labels on the KITTI dataset [10] and KITTI-CARLA dataset [7]. The experimental results demonstrate that our proposed ADL method not only achieves impressive performance compared to manual labeling but also exhibits more robust and accurate results than both traditional methods and state-of-the-art self-supervised methods.
@inproceedings{10341687, author = {Ma, Fulong and Liu, Yang and Wang, Sheng and others}, booktitle = {2023 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS)}, title = {Self-Supervised Drivable Area Segmentation Using LiDAR's Depth Information for Autonomous Driving}, year = {2023}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {41-48}, keywords = {Point cloud compression;Training;Laser radar;Uncertainty;Semantic segmentation;Roads;Training data}, doi = {10.1109/IROS55552.2023.10341687} }
2022
-
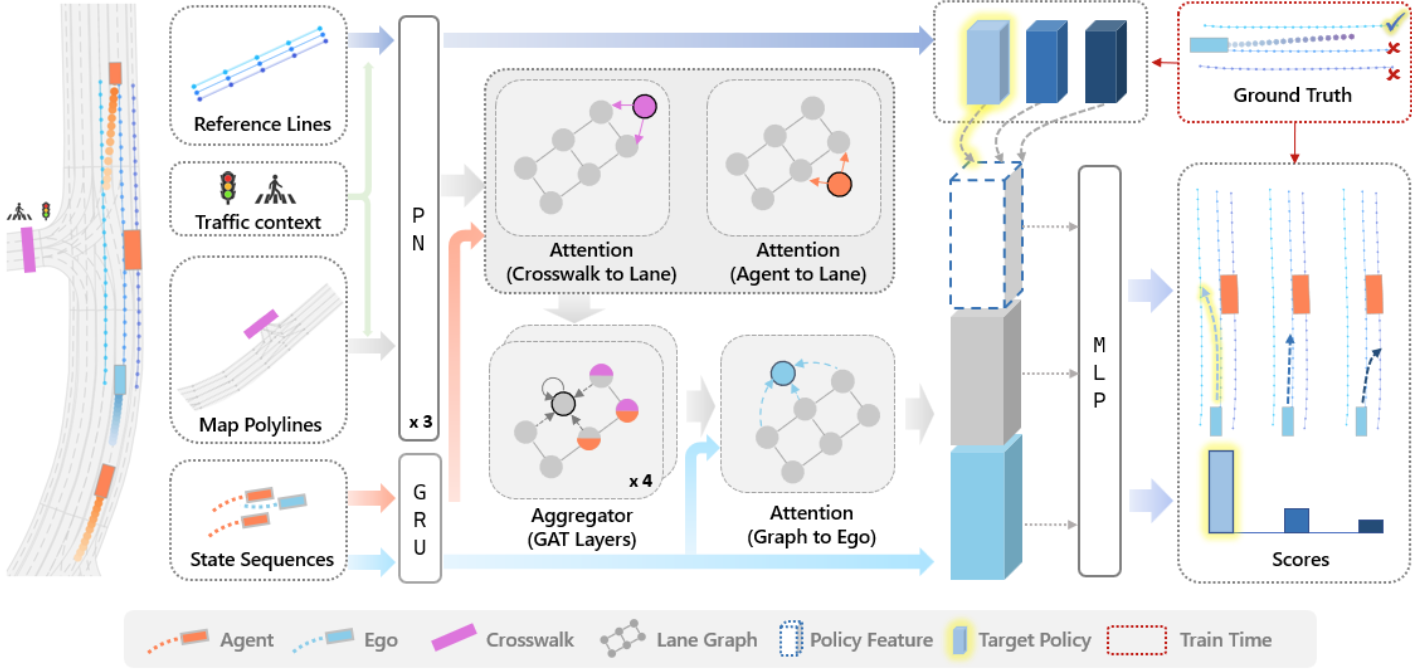 MPNP: Multi-Policy Neural Planner for Urban DrivingJie Cheng, Ren Xin, Sheng Wang, and othersIn 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2022
MPNP: Multi-Policy Neural Planner for Urban DrivingJie Cheng, Ren Xin, Sheng Wang, and othersIn 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2022Our goal is to train a neural planner that can capture diverse driving behaviors in complex urban scenarios. We observe that even state-of-the-art neural planners are struggling to perform common maneuvers such as lane change, which is rather natural for human drivers. We propose to explore the multi-modalities in the planning problem and force the neural planner to explicitly consider different policies. This is achieved by generating the future trajectories conditioned on every possible reference line, which could simply be the centerline of the surrounding lanes. We find this simple strategy yet enables the planner to perform rich and complex behaviors. We train our model using real-world driving data and demonstrate the effectiveness of our method through both open-loop and closed-loop evaluations.
@inproceedings{MPNP, author = {Cheng, Jie and Xin, Ren and Wang, Sheng and others}, booktitle = {2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS)}, title = {MPNP: Multi-Policy Neural Planner for Urban Driving}, year = {2022}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {10549-10554}, keywords = {Force;Data models;Behavioral sciences;Trajectory;Planning;Intelligent robots}, doi = {10.1109/IROS47612.2022.9982111} } - A flight test based deep learning method for transition heat flux prediction in hypersonic flowHaijie Ren, Sheng Wang, and othersPhysics of Fluids, May 2022
Computational fluid dynamics predictions based on machine learning methods have become an important area of turbulence and transition research. However, the otherwise efficient and low-cost transition models based on Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes (RANS) methods have limited capability for dealing with hypersonic conditions, owing to the strong compressibility and multimodal features that are then present. This paper develops an augmented method for transition heat flux prediction. A deep neural network (DNN) is trained using flight test data from the China Aerodynamics Research and Development Center. The subject of the flight test is an inclined blunt cone on which temperature sensors are mounted. The training data consist of RANS solutions and flight test data, with the input being the mean strain/rotation rate tensor from RANS and the output the heat flux values from the flight test. The trained DNN model based on the RANS results can give heat flux values with similar accuracy to those from the flight test. For the blunt cone, the trained DNN model can accurately forecast the heat distribution caused by the Mack mode and the cross-flow transition under various inflow conditions, and the errors in the prediction results are all within 15%. Furthermore, the generalizability of the trained DNN model is also verified on an elliptic cone under different inflow conditions. This paper provides a new transition prediction approach with low computational cost and high accuracy. The proposed method solves the problem that the transition model fails in some working conditions and avoids re-modifying empirical criteria in the RANS model. It has both advantages of a transition model and flight tests and maintains the excellent potential for application.
@article{10.1063/5.0093438, author = {Ren, Haijie and Wang, Sheng and others}, title = {{A flight test based deep learning method for transition heat flux prediction in hypersonic flow}}, journal = {Physics of Fluids}, volume = {34}, number = {5}, pages = {054106}, year = {2022}, month = may, issn = {1070-6631}, doi = {10.1063/5.0093438}, eprint = {https://pubs.aip.org/aip/pof/article-pdf/doi/10.1063/5.0093438/16632627/054106\_1\_online.pdf} } -
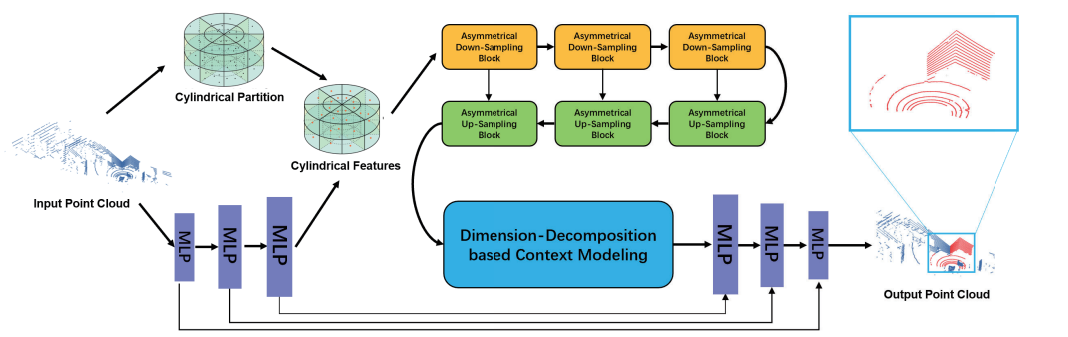 An Automatic Multi-LiDAR Extrinsic Calibration Algorithm Using Corner PlanesFulong Ma, Sheng Wang, and othersIn 2022 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), May 2022[Best paper finalist]
An Automatic Multi-LiDAR Extrinsic Calibration Algorithm Using Corner PlanesFulong Ma, Sheng Wang, and othersIn 2022 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), May 2022[Best paper finalist]With the development of autonomous driving, more autonomous vehicles are equipped with multiple sensors to perform better. For multi-sensor systems, accurate extrinsic calibration is a prerequisite for perception and localization systems. Extrinsic calibration aims to transform two or more sensors’ coordinates into a unified spatial coordinate system. Sensors usually need to be calibrated after installation to ensure accurate measurements. Most existing methods require special calibration markers or rely heavily on additional sensors to solve this problem. Recently, researchers have proposed a novel method that can calibrate extrinsic parameters using the common corners in surroundings to solve the multi-LiDARs extrinsic calibration problem, three linearly independent planar surfaces of the corner are utilized to compute the extrinsic parameters. However, this method is relatively inefficient and requires manual operation, especially in some hard scenes. To overcome this problem, we propose using the learning-based method to segment corners, improving efficiency and convenience without losing accuracy. By introducing learning-based corner segmentation method, we can achieve “one-click” extrinsic calibration, that is, there is no need to prepare auxiliary markers, there is no need to collect a large amount of data and data preprocessing, and the external parameters can be automatically calibrated.
@inproceedings{10011672, author = {Ma, Fulong and Wang, Sheng and others}, booktitle = {2022 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO)}, title = {An Automatic Multi-LiDAR Extrinsic Calibration Algorithm Using Corner Planes}, year = {2022}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {235-240}, note = {[Best paper finalist]}, keywords = {Training;Laser radar;Semantic segmentation;Training data;Transforms;Tail;Sensor systems}, doi = {10.1109/ROBIO55434.2022.10011672} }